Restored giant kelp forests can buffer against climate change threats
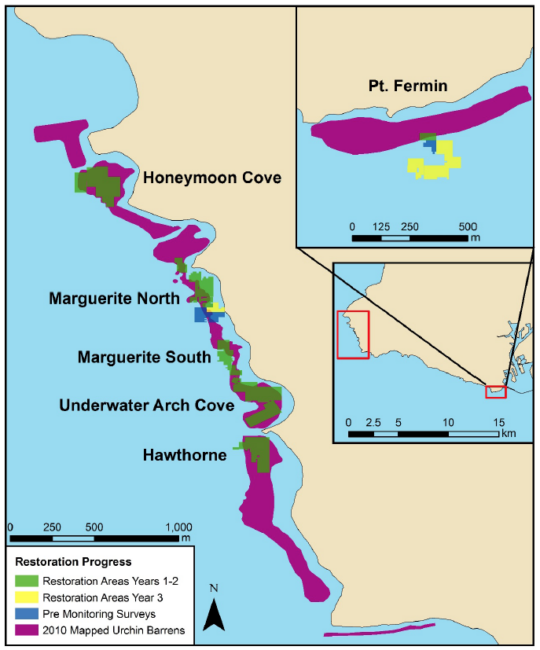
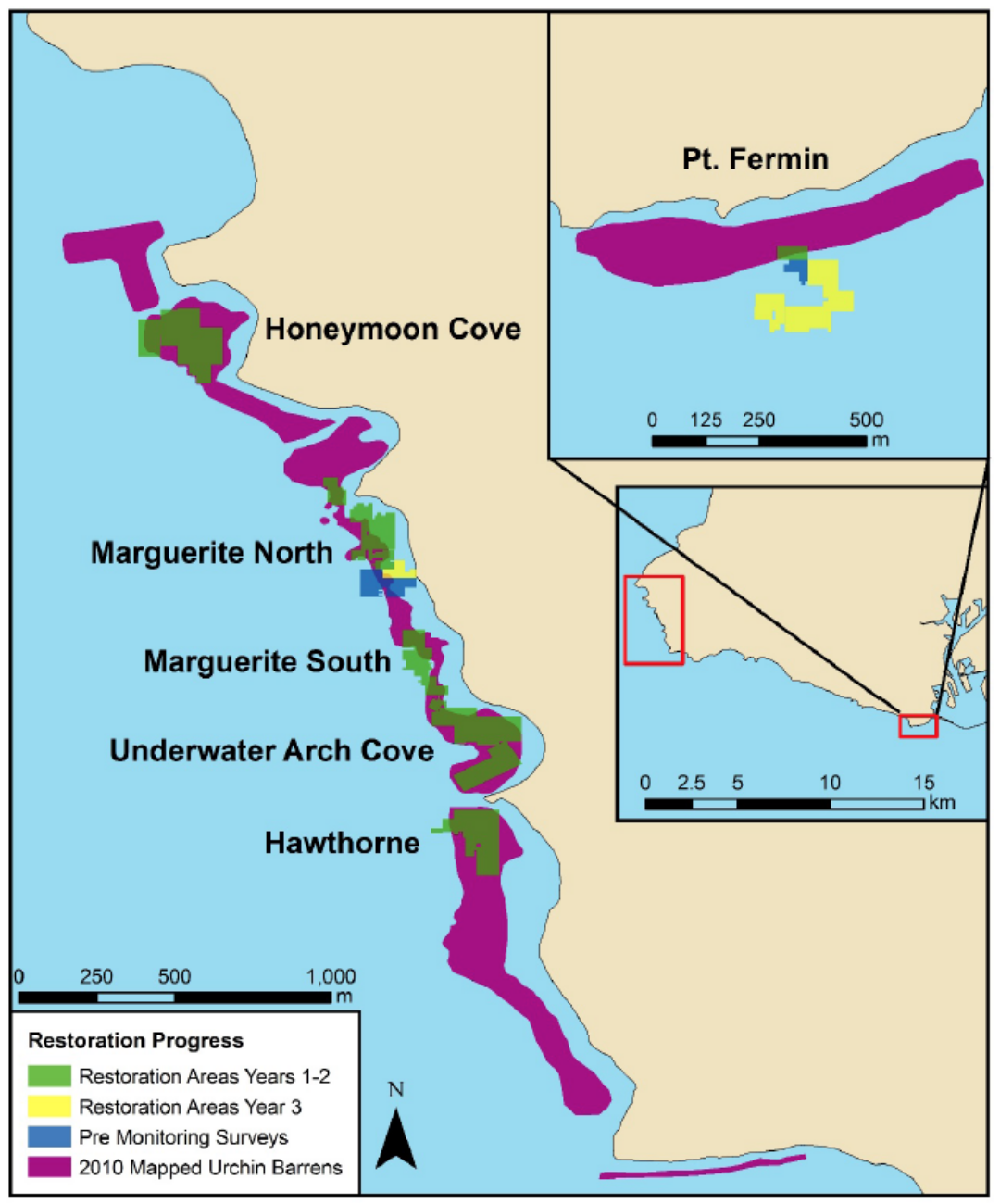
As climate changes, coastal managers are concerned with accelerating shoreline erosion rates, amplified wave heights, and the disruption of coastal resources due to ocean acidification. Kelp and other aquatic vegetation are thought to reduce the force of ocean waves and balance the nearby seawater chemistry through their uptake of carbon dioxide. University of Southern California (USC) Sea Grant funded a study to determine if restoring kelp forest habitats poses additional benefits for wave attenuation and balancing of seawater chemistry. The study measured water column chemistry across two differing kelp restoration sites in Palos Verdes and Monterey, California.
Key Results:
- Kelp forests help with mixing: they measurably dampen the force of ocean waves and currents in their local vicinity, leading to water mixture extending to the ocean bottom and thus improving conditions for organisms that may be susceptible to hypoxia and ocean acidification
- These effects were documented before and after a successful kelp bed restoration
Project Impacts & Application:
- Results were included in a 2021 Ocean Protection Council policy guidance document on Climate Change and Marine Protected Areas
- The project team presented at the Western Society of Naturalists Presidential Symposium and the Ocean Sciences Meeting in San Diego
Principal Investigators:
- Kerry J. Nickols, Ph.D., California State University, Northridge
- Brian Gaylord, Ph.D., University of California, Davis
- Tom Ford, The Bay Foundation
Funding:
NOAA, 2018-2020
Additional Info:
- https://www.santamonicabay.org/explore/in-the-ocean/kelp-forest-restoration/
- https://opc.ca.gov/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Climate-Resilience-and-Californias-MPA-Network-2021_final_ADA_OST.pdf
- Traiger, S.B., Cohn, B., Panos, D., Daly, M., Hirsh, H.K., Martone, M., Gutierrez, I., Mucciarone, D.A., Takeshita, Y., Monismith, S.G., Dunbar, R.B. and Nickols, K.J. (2022), Limited biogeochemical modification of surface waters by kelp forest canopies: Influence of kelp metabolism and site-specific hydrodynamics. Limnol Oceanogr, 67: 392-403. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.11999
Access our Publications Database to view publications from this project or other related topics