This is my archive
Autistic children have poorer oral health and greater oral care challenges, which are often associated with sensory overresponsivity, than neurotypical peers. It is important to identify innovative solutions enabling dentists to successfully perform standard clinic-based procedures for this population. Read More

The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic has exacerbated existing health disparities in the United States [1]. After the onset of the pandemic, hospitals empirically screened patients for SARS-CoV-2. Many children were incidentally found to have SARS-CoV-2 though the primary reason for their encounter may have been unrelated [2]. We aimed to describe sociodemographic characteristics of infants less than one year of age diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 alongside healthcare utilization while distinguishing between those with confirmed versus incidental infection. Read More

We assessed the current performance and cost-effectiveness of universal testing for tuberculosis in pregnancy at a single safety net hospital. Read More
Online longitudinal surveys may be subject to potential biases due to sample attrition. This study was designed to identify potential predictors of attrition using a longitudinal panel survey collected during the COVID-19 pandemic. Attrition in this longitudinal panel survey was not random. Besides commonly identified demographic factors that contribute to panel attrition, COVID-19 presented novel opportunities to address sample biases by correlating attrition with additional behavioral and HRQoL factors in a constantly evolving environment. While age, ethnicity, and survey difficulty consistently predicted attrition, other factors, such as COVID-19 experience, changes of employment, productivity, physical health, mental health, and financial situation impacted panel attrition during the pandemic at various degrees. Read More

The objective of this study was to examine the prevalence of diagnosed venous thromboembolism (VTE) in infants Read More

The outbreak of the pandemic COVID-19 (Coronavirus) has resulted in various international and national strategies, including non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) such as social distancing and travel bans, which have purportedly mitigated the health loss due to the pandemic but also given rise to a severe economic crisis. Both factors, the pandemic and the NPIs, can be expected to have an impact on the Health-Related Quality-of-Life (HRQoL) of the population. The objective of this study was to estimate the impact on HRQoL of the Swedish adult population during the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic. Read More

The use of therapeutic hypothermia (TH) for mild hypoxic–ischaemic encephalopathy (HIE) remains controversial and inconsistent. We analysed trends in TH and maternal and infant characteristics associated with short-term outcomes of infants with mild HIE. Read More

The purpose of this study was to determine the value of early exome sequencing (eES) relative to the current typical care (TC) in the diagnosis of newborns with suspected severe mitochondrial disorders (MitD). The results from the study found that trio and singleton eES are cost-effective and cost-minimizing alternatives to current TC in diagnosing newborns suspected of having a severe MitD. Read More

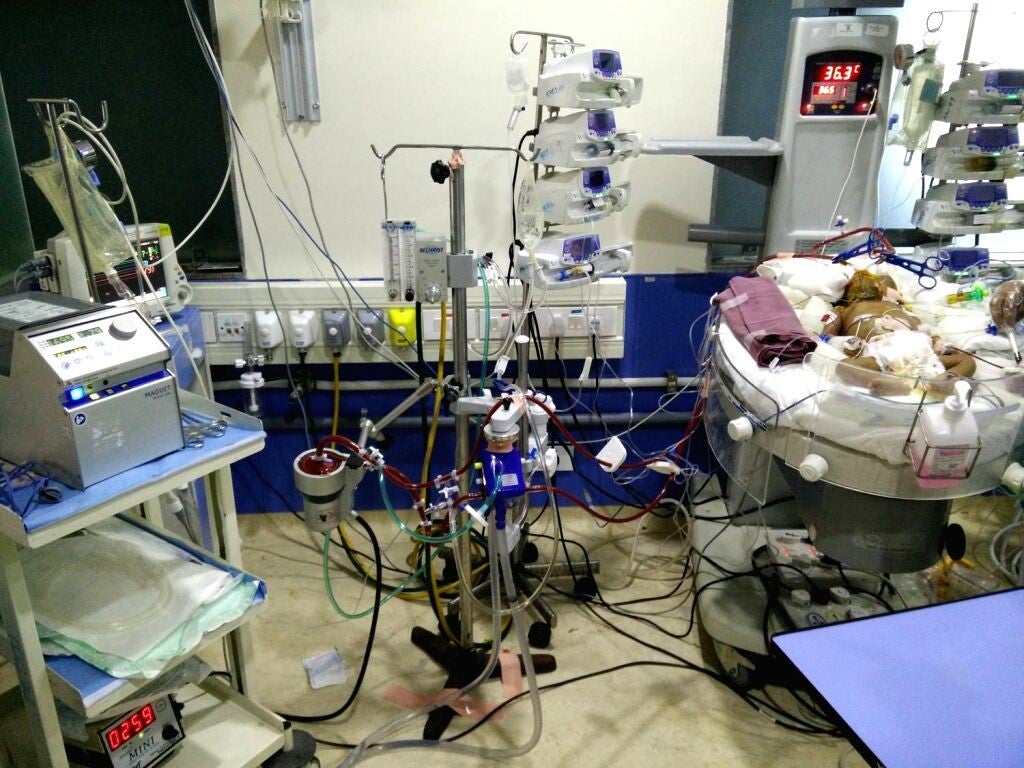
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is a lifesaving treatment for critically ill neonates. While there is some information on hospital readmissions and survival in non-neonatal pediatric and adult ECMO patients, there is little published data reporting readmission for neonatal ECMO survivors. The goals of this analysis were to (1) establish early and late readmission rates, (2) identify associated demographic, socioeconomic, and co-morbidity factors, (3) and to determine prognosticators regarding readmission in ECMO survivors. Read More
Throughout the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic, susceptible-infectious-recovered (SIR) modeling has been the preeminent modeling method to inform policy making worldwide. Nevertheless, the usefulness of such models has been subject to controversy. An evolution in the epidemiological modeling field is urgently needed, beginning with an agreed-upon set of modeling standards for policy recommendations. The objective of this article is to propose a set of modeling standards to support policy decision making. Read More









