Deep thinking in the brain may be spurred by stories with moral quandaries
Everyone has at least a few non-negotiable values. These are the things that, no matter what the circumstance, you’d never compromise for any reason — such as “I’d never hurt a child,” or “I’m against the death penalty.”
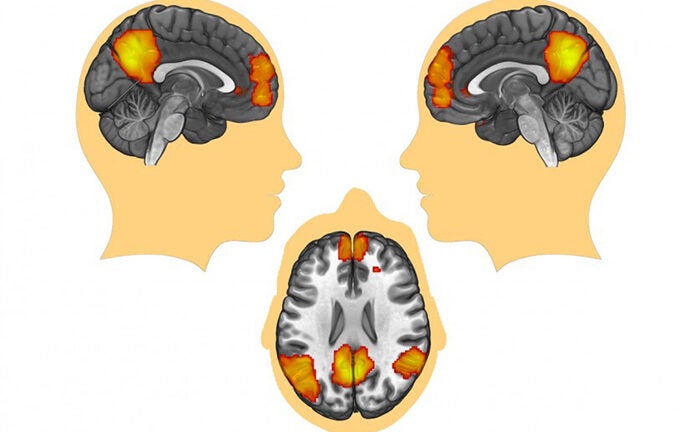
Real-time brain scans show that when people read stories that deal with these core, protected values, the “default mode network” in their brains activates.
This network was once thought of as merely the brain’s autopilot, since it has been shown to be active when you’re not engaged by anything in the outside world. Studies like this one, however, suggest that it’s actually working to find meaning in the narratives.
“The brain is devoting a huge amount of energy to whatever that network is doing. We need to understand why,” said Jonas Kaplan of the USC Dornsife Brain and Creativity Institute. Kaplan was the lead author of the study, which was published on Jan. 7 in the journal Cerebral Cortex.
Kaplan thinks that it’s not just that the brain is presented with a moral quandary, but rather that the quandary is presented in a narrative format.
Reading blog posts and brain scans
To find relevant stories, the researchers sorted through 20 million blog posts using software developed at the USC Institute for Creative Technologies.
“We wanted to know how people tell stories in their daily lives. It was kind of like finding stories in their natural habitat,” said Kaplan, who is also assistant professor (research) of psychology.

Jonas Kaplan of the Brain and Creativity Institute. Photo by John Livzey.
That 20 million was pared down to 40 stories that each contained an example of a crisis involving a potentially protected value: cheating on a spouse, having an abortion, crossing a picket line, or getting in a fight.
Those stories were translated into Mandarin Chinese and Farsi, and then read by American, Chinese and Iranian participants in their native language while their brains were scanned by fMRI. They also answered general questions about the stories while being scanned.
Stories that participants said involved values that were protected to them activated the default mode network in their brain to a greater degree. In addition, the level of activation varied from culture to culture. On average, Iranians showed the greatest level of activation in the study, while the Chinese participants showed the least.
“Stories appear to be a fundamental way in which the brain organizes information in a practical and memorable manner. It is important to understand the neural mechanisms required to do this, and this study is a step in that direction,” said Antonio Damasio, senior author of the study. Damasio is co-director of the Brain and Creativity Institute, holder of the David Dornsife Chair in Neuroscience and a professor of psychology and neurology.
Biological roots of values
It’s not yet clear whether a value either is or is not protected, or whether the sacredness of a value is on a sliding scale. But in a nation where political beliefs are growing more polarized and entrenched, it’s important to understand what biological processes lie at the root of these values, Kaplan said.
“People will often hold political values as protected values and protected values are at the root of many political conflicts around the world, which is why they’re interesting to us,” he said.
Kaplan’s coauthors include researchers from the USC Dornsife Brain and Creativity Institute and the USC Institute for Creative Technologies.